Definition Of Water Cycle Absorption
There are a lot of processes involved in the water cycle and all of these are. Removal of water from the soil by roots.
 What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
It is the invisible process of evaporation that changes liquid and frozen water into water-vapor gas which then floats up into the skies to become clouds.

Definition of water cycle absorption. What is the Water Cycle. This process differs from absorption in which a fluid the absorbate is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid the absorbent. Water cycle also called hydrologic cycle cycle that involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth-atmosphere system.
Land-based cycle transfers phosphorus from soil to plants to animals. On the other hand ice become to water as liquid or gas as vapor. During the cycle process water is going through the changes and sometimes it can be solid like ice liquid like water or as a gas like vapor.
Water cycle on earth changing every day and the repeating changes makes a cycle. Absorption on the other hand goes deeper involving the entire volume of the absorbent. The water cycle describes how water moves throughout the Earth.
For the water cycle to work water has to get from the Earths surface back up into the skies so it can rain back down and ruin your parade or water your crops or yard. Definition The water cycle or hydrologic cycle describes the complex systems that allow water to move across the Earth and atmosphere. Absorption of water by the soil.
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon in which particles or molecules bind to the top layer of material. Drainage of water on the ground. Infiltration is the absorption of water by the soil and rock of the upper level of the Earths crust and is very much dependent on environmental factors such as soil or rock depth vegetation levels saturation levels and porosity.
Absorption of Water and Electrolytes The small intestine must absorb massive quantities of water. Evaporation of water from the surface of the soil. Controls the distribution of Earths waterCirculates through four spheres of EarthHas no starting pointEarths water is always in movementWater is always changing states.
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms ions or molecules from a gas liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. Absorption is the filling of pores or holes in a substance. A normal person or animal of similar size takes in roughly 1 to 2 liters of dietary fluid every day.
Although the total amount of water within the cycle remains essentially constant its distribution among the various processes is. Absorption in the water cycle is the process when surface water is absorbed into the ground. The most basic step of the water cycle is the change of state of water as a liquid gas or solid in the atmosphere.
First water transpires from plants and enters the atmosphere as water vapor. Its then cycled back to soil again. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent.
Water from Earths oceans lakes and rivers also evaporates into the atmosphere. In the atmosphere the water forms clouds. It mainly cycles through the soil water and sediments.
The absorption cycle enjoys the benefits of requiring a fraction of the electrical input plus uses the natural substances ammonia and water instead of ozone depleting halocarbons. Absorption of water by the top layer of the soil. An absorption cycle can be viewed as a mechanical vapor-compression cycle with the compressor replaced by a generator absorber and liquid pump.
That means there is a land-based phosphorus cycle and water-based phosphorus cycle. The evaporation from Earths waterways and from plants via transpiration is collectively known as evapotranspiration. Again the water vapor can be liquid water or ice too.
Intermediary water cycle steps provide a bridge between water landing on the Earths surface and water vapor rising into the troposphere. Of the many processes involved in the water cycle the most important are evaporation transpiration condensation precipitation and runoff. The water cycle is responsible for the continuous movement of water in various phases around the Earth.
 Water Cycle The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Water Cycle The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
 Nitrogen Cycle Project Students Will Love Fun Way To Assess Student Understanding Of The Material Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Diy Fish Tank
Nitrogen Cycle Project Students Will Love Fun Way To Assess Student Understanding Of The Material Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Diy Fish Tank
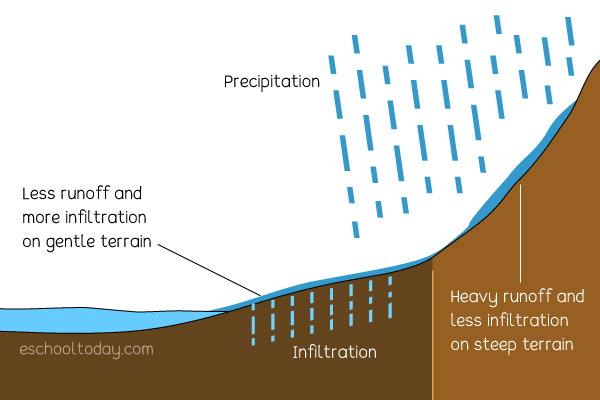 The Runoff Stage Of The Water Cycle Eschooltoday
The Runoff Stage Of The Water Cycle Eschooltoday
 Absorption Of Water By Plants Ikenschoool Youtube
Absorption Of Water By Plants Ikenschoool Youtube
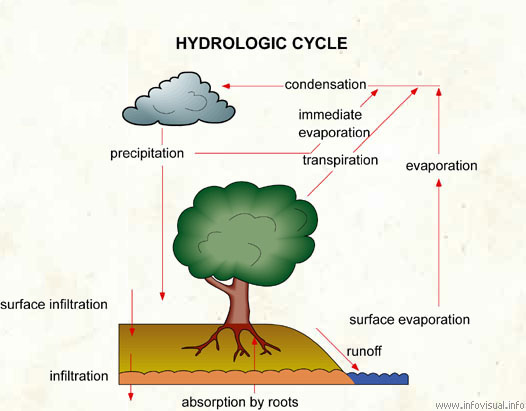 Hydrologic Cycle Visual Dictionary
Hydrologic Cycle Visual Dictionary
 What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
 What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
 Foldable To Use For Teaching Light Vocabulary Absorption Reflection Refraction There Are Two Vers Science Notebooks Interactive Science Notebook Vocabulary
Foldable To Use For Teaching Light Vocabulary Absorption Reflection Refraction There Are Two Vers Science Notebooks Interactive Science Notebook Vocabulary
 Biogeochemical Cycles Worksheets Middle School Science Resources Earth Science Lessons High School Science
Biogeochemical Cycles Worksheets Middle School Science Resources Earth Science Lessons High School Science
 What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
What Absorbs Water Absorption For Kids Little Bins For Little Hands
 Absorption Of Water In Plants With Diagram
Absorption Of Water In Plants With Diagram
 Absorption By Roots Icse Solutions For Class 10 Biology A Plus Topper Http Www Aplustopper Com Absorption Roots Icse Sol Biology Class Biology Solutions
Absorption By Roots Icse Solutions For Class 10 Biology A Plus Topper Http Www Aplustopper Com Absorption Roots Icse Sol Biology Class Biology Solutions
 Absorption Experiment Science Projects Preschool Science Elementary Science
Absorption Experiment Science Projects Preschool Science Elementary Science
 The Difference Between Evaporation And Condensation And Their Importance In Creating Weather Events Evaporation Condensation Weather And Climate
The Difference Between Evaporation And Condensation And Their Importance In Creating Weather Events Evaporation Condensation Weather And Climate
 Pin By Erin Barry On Edee 500 Education Weather And Climate Elementary Education Classroom
Pin By Erin Barry On Edee 500 Education Weather And Climate Elementary Education Classroom
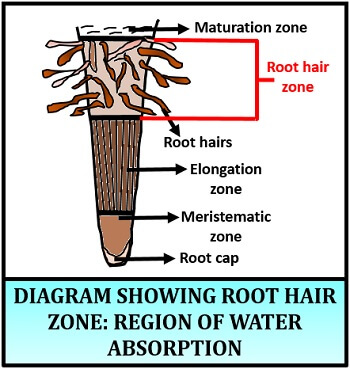 Absorption Of Water In Plants Definition Types Mechanism Biology Reader
Absorption Of Water In Plants Definition Types Mechanism Biology Reader
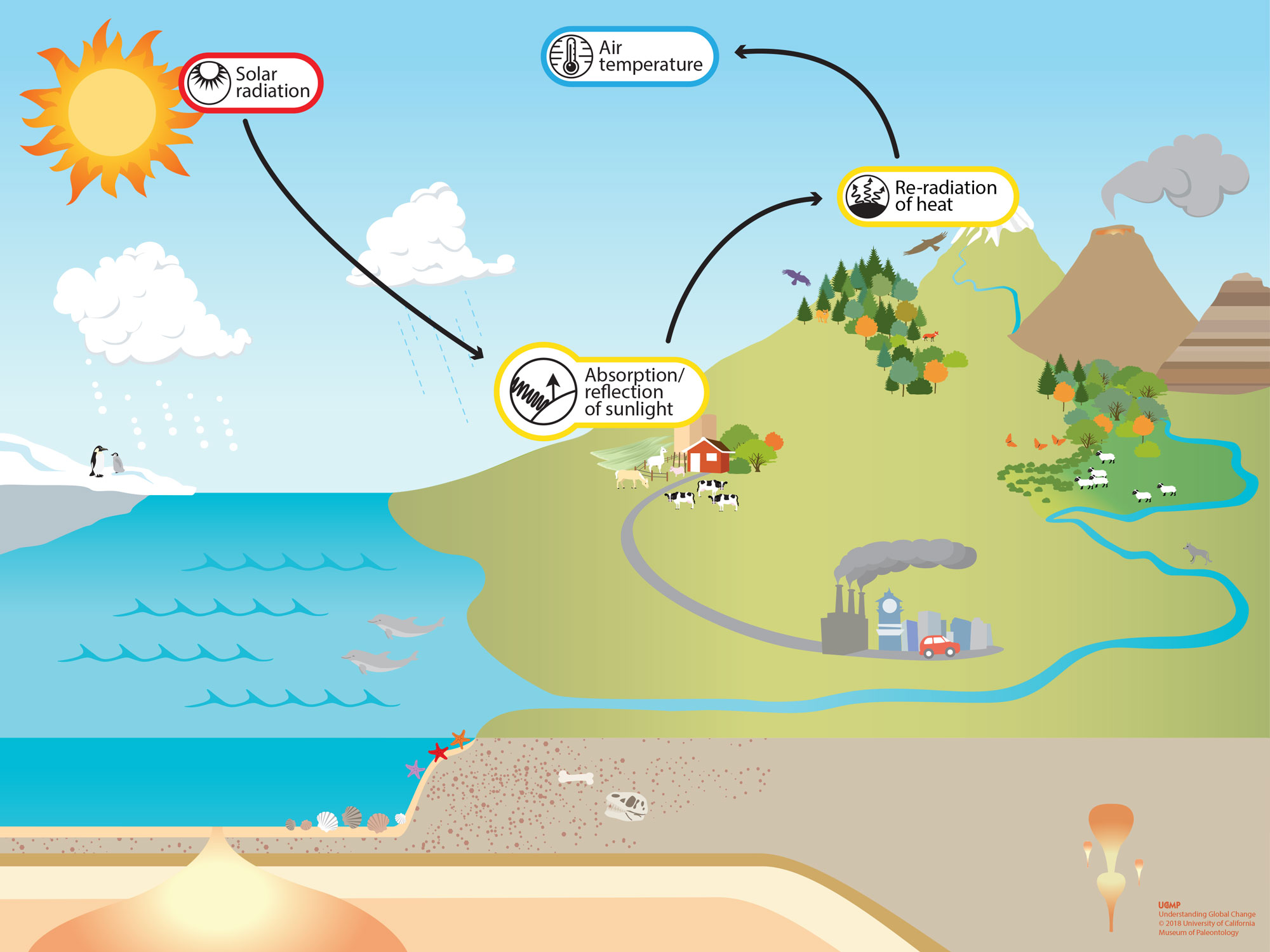 Absorption Reflection Of Sunlight Understanding Global Change
Absorption Reflection Of Sunlight Understanding Global Change
 Apoplast Vs Symplast Biology Class Plant Physiology Physiology
Apoplast Vs Symplast Biology Class Plant Physiology Physiology
Post a Comment for "Definition Of Water Cycle Absorption"