Def Of Nuclear Binding Energy
This is more commonly known as ionization energy. This energy difference accounts for the stability of the atom.
 What S The Difference Between Nuclear Fission And Fusion
What S The Difference Between Nuclear Fission And Fusion
The protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus are held together by the nuclear forces strong force.
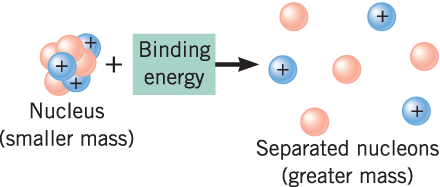
Def of nuclear binding energy. Proton BEs remove protons from the nucleus. In physics binding energy is the minimum energy required to either separate an electron from an atom or to separate the protons and neutrons of an atomic nucleus. Nuclear binding energy is the energy required to separate an atomic nucleus completely into its constituent protons and neutrons or equivalently the energy that would be liberated by combining individual protons and neutrons into a single nucleus.
The definition of binding energy per nucleon is the amount of energy required to break the nucleus into protons and neutrons again. It is equal to. At atomic level the atomic binding energy of the atom derives from electromagnetic interaction of electrons in the atomic cloud and nucleons protons in the nucleus.
General Physics the energy required to remove a particle from a system esp an electron from an atom. Binding Energy The binding energy is equal to the amount of energy released in forming the nucleus and is therefore given by 1032 E b m c 2. A graph of binding energy per nucleon BEN versus atomic number A implies that nuclei divided or combined release an enormous amount of energy.
The mass of a nucleus is always less than the sum of masses of the constituent protons and neutrons. The figure below shows the binding energy for each element against their atomic number Z. The binding energy BE of a nucleus is the energy needed to separate it into individual protons and neutrons.
2012 Farlex Inc. Types of Binding Energy. Binding energy can calculate the expected mass of any nuclei from the knowledge of the nuclear composition like masses of the electron proton and neutron particles or nucleon and Einstein relativity equation or formula in physics or chemistry.
General Physics the energy that must be supplied to a stable nucleus before it can undergo fission. The larger the binding energy the more difficult it would be to separate subatomic particles from their nucleus. This binding energy can be calculated from the Einstein relationship.
The minimum energy needed to dissociate an atomic nucleus into neutrons and protonsneutron binding energies BEs remove neutrons from the nucleus. Binding energy is also known as separation energy. Electron BEs remove electrons.
Experimental results indicate that the binding energy for a nucleus with mass number A 8 is roughly proportional to the total number of nucleons in the nucleus A. The amount of energy required to achieve this is called nuclear binding energy. The difference is a measure of the nuclear binding energy which holds the nucleus together.
Nuclear binding energy The amount by which the mass of an atom is less than the sum of the masses of its constituent protons neutrons and electrons expressed in units of energy. At nuclear level the nuclear binding energy is the energy required to disassemble to overcome the strong nuclear force a nucleus of an atom into its component parts protons and neutrons. The binding energy BE of a nucleus is equal to the amount of energy released in forming the nucleus or the mass defect multiplied by the speed of light squared.
The atomic binding energy is the energy required to disassemble an atom into free electrons and a nucleus. This notable difference is a measure of the nuclear binding energy which is a result of forces that hold the nucleus together. In terms of atomic masses BE Zm 1 H Nmn m A X c2 where m 1 H is the mass of a hydrogen atom m A X is the atomic mass of the nuclide and mn is the mass of a neutron.
It is equal to the mass defect less the quantity of energy or mass released when a bound system is created. To attain this a certain amount of energy is put into the system. In physics and chemistry binding energy is the smallest amount of energy required to remove a particle from a system of particles or to disassemble a system of particles into individual parts.
Thus we can define nuclear binding energy as The minimum energy required to separate nucleons into its constituent protons and neutrons and is given by-E_bleft Delta mright c2. Nuclear binding energy mc2 For the alpha particle m 00304 u which gives a binding energy of 283 MeV.
 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Britannica
Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Britannica
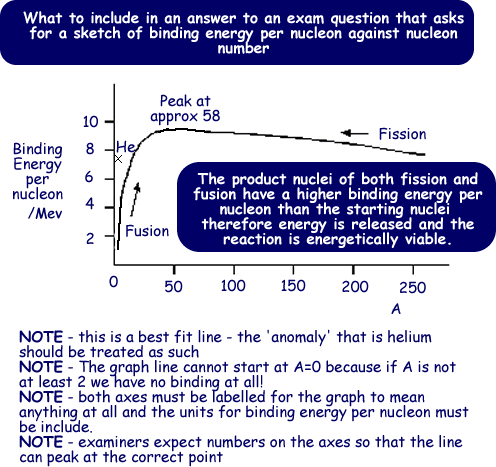
 Binding Energy Curves Nuclear Energy Physics Class 2021 Video Study Com
Binding Energy Curves Nuclear Energy Physics Class 2021 Video Study Com
 Nuclear Binding Energy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Nuclear Binding Energy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
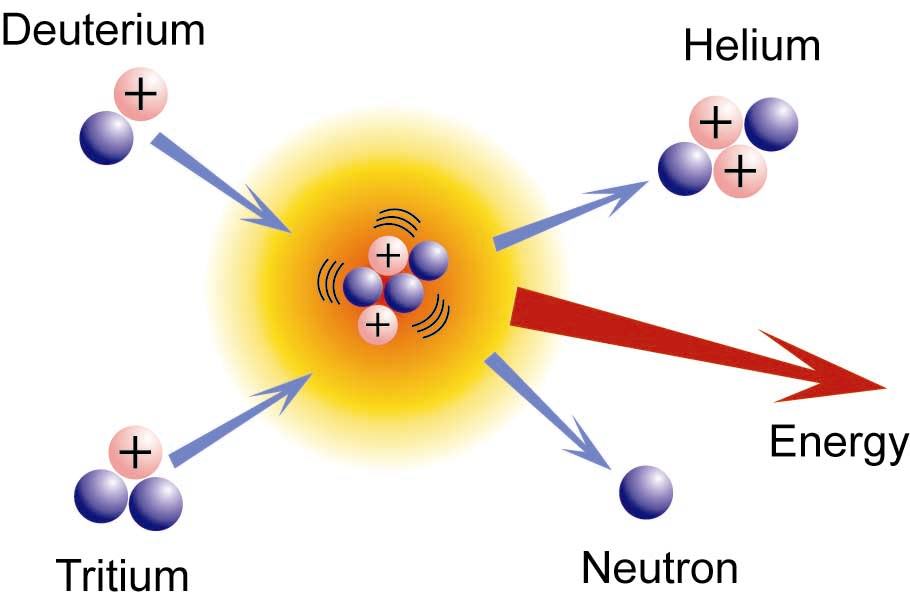 What Is Binding Energy Universe Today
What Is Binding Energy Universe Today
 Binding Energy Definition Characteristics Nuclear Power Net
Binding Energy Definition Characteristics Nuclear Power Net
 Nuclear Energy Definition Sources Uses Facts Britannica
Nuclear Energy Definition Sources Uses Facts Britannica
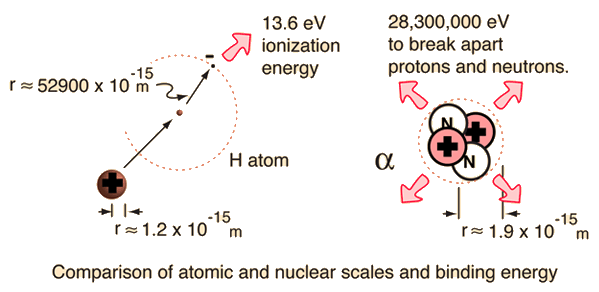 Copy Of What Is Nuclear Binding Energy Sutori
Copy Of What Is Nuclear Binding Energy Sutori
 Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Unit 26 Nucleus Is Defined As The Central Core Of An Atom That Is Positively Charged Ppt Download
Properties Of Nucleus 26 2 Binding Energy And Mass Defect Unit 26 Nucleus Is Defined As The Central Core Of An Atom That Is Positively Charged Ppt Download
 Nuclear Binding Energy Per Nucleon Mass Defect Problems Nuclear Chemistry Youtube
Nuclear Binding Energy Per Nucleon Mass Defect Problems Nuclear Chemistry Youtube
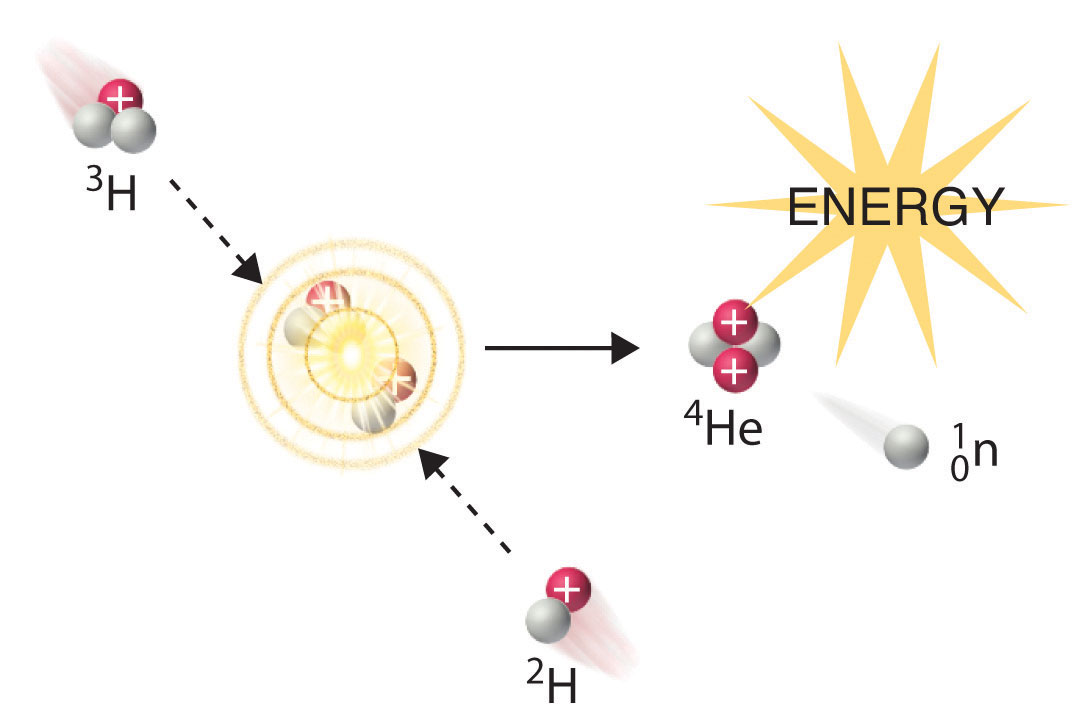 Fission And Fusion Chemistry Libretexts
Fission And Fusion Chemistry Libretexts
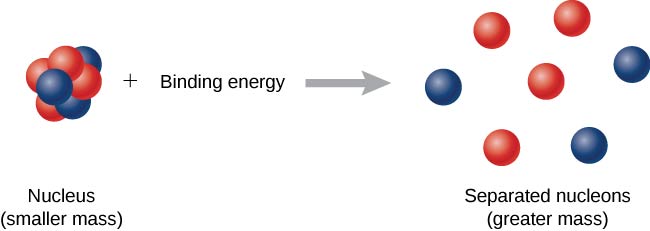 10 3 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Libretexts
10 3 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Libretexts
How To Calculate The Binding Energy Per Nucleon Quora
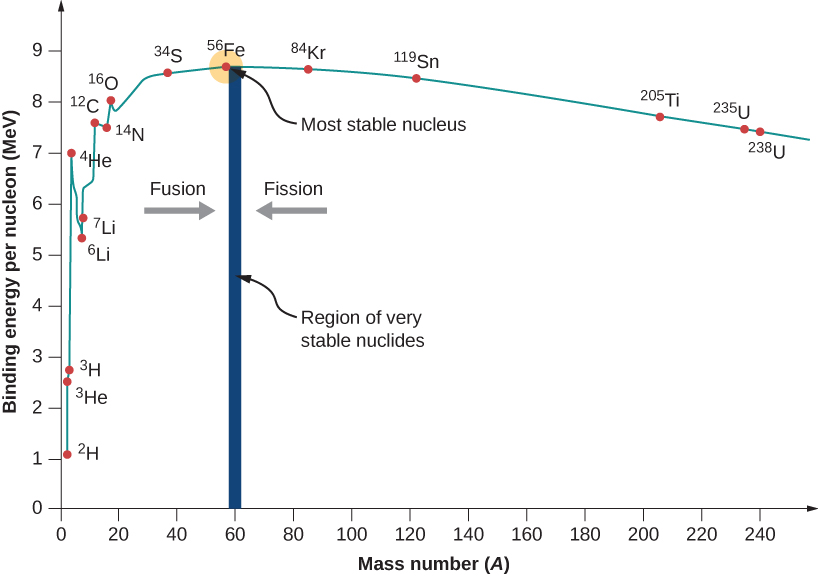 10 3 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Libretexts
10 3 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Libretexts
 Copy Of What Is Nuclear Binding Energy Sutori
Copy Of What Is Nuclear Binding Energy Sutori
 Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Britannica
Nuclear Binding Energy Physics Britannica


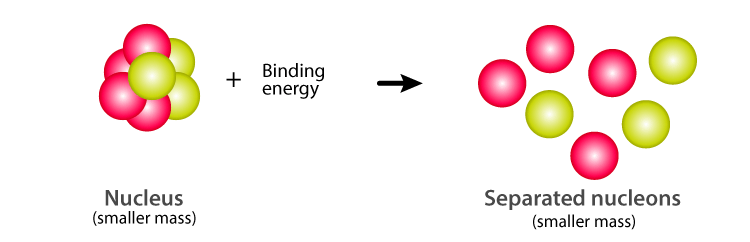
Post a Comment for "Def Of Nuclear Binding Energy"